Original study
Background: The growing frequency of fractures associated with osteoporosis, the significant costs of their treatment, disability and increased mortality make it an important and urgent task to optimize the diagnosis and treatment of osteoporosis in the Russian Federation.
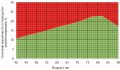
Aim: The aim of this study was analyzed of using modern diagnostic criteria for osteoporosis by specialists when they making a clinical decision to initiate treatment for osteoporosis, including an estimate of the 10-year probability of fractures according to FRAX.
Materials and methods: The study was conducted in the city consultative and diagnostic center for the prevention of osteoporosis, St. Petersburg. The register of the osteoporosis center for 2018–2021 was used to select patients for the study. Based on the analysis of registry data, a sample of 362 patients with newly diagnosed osteoporosis was obtained. In the resulting sample, the existing FRAX value was assessed on the therapeutic intervention threshold graph, all of them analyzed the primary medical documentation, as well as the available DXA densitometry data.
Results: In this study, we assessed the place of FRAX 10-year risk of major osteoporotic fractures in the clinical decision of an osteoporosis specialist to start anti-osteoporosis therapy, in this case taken as the «gold standard». The study found that a positive FRAX score had a high predictive value of 100%. In contrast, the negative predictive value was very low (19.5%): a FRAX value below the intervention threshold did not guarantee a truly low fracture risk and no need to start osteoporosis treatment.
Conclusion: Despite the fact that both densitometry and FRAX have significant limitations in use, and cannot identify all patients with a high risk of fractures, their combined use increases the prognostic value of the methods. FRAX technology in routine practice allows, in addition to clinical and instrumental methods for diagnosing high-risk fractures, to identify candidates for the treatment of osteoporosis, and should be used in accordance with clinical recommendations.
Background. Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is an autoimmune inflammatory disease of connective tissue with a polysyndromic clinical picture. One of the factors that significantly affect the quality of life of such patients is the involvement of the musculoskeletal system. A small number of studies were aimed at studying osteoporosis and body composition in patients with SSc, however, the clinical heterogeneity of the disease, a small number of patients included in the studies do not allow to draw unambiguous conclusions about the frequency of various phenotypes of body composition, their relationship and factors affecting their occurrence.
Aim. To study the body composition and to establish the frequency of isolated and combined pathological phenotypes in women with SSс and to determine the factors associated with the muscle mass.
Materials and methods. 85 postmenopausal women (46 with SSc, 39 without rheumatic pathology) were included. Questionnaires, anthropometric measurements, assessment of nutritional status by MNA, dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry of the whole body, lumbar spine, femoral neck and total hip were carried out. Correlation and univariate linear regression analyses were performed to identify factors related to appendicular muscle mass.
Results. Normal body composition was found in 13.0% of patients with SSс and 25.6% — in the control, isolated and combined pathological phenotypes were detected in 34.8% and 52.2% women with SSс and in 61.5% and 12.8% in the group without rheumatic diseases, respectively. Combined pathological phenotypes, phenotypes with the presence of sarcopenia and/or osteoporosis were significantly more often in SSc patients (p< 0.001), but the frequency of obesity did not differ (69.6% and 64.1%, respectively). Negative correlations were revealed between the value of appendicular muscle mass and the presence of osteolysis of the nail phalanges (Rs=-0.23), the cumulative dose of glucocorticoids (GC) (Rs=-0.43) and direct — with the value of the femoral neck BMD (Rs=0.47), nutritional status by MNA (Rs=0.51), BMI (Rs=0.70), the circumference of the shoulder of the non-dominant arm (Rs=0.68), waist (Rs=0.66), hips (Rs=0.72) and lower leg of the non-dominant leg (Rs=0.81), p< 0.05. Univariate linear analysis confirmed the presence of positive associations between the appendicular muscle mass and proximal hip BMD, BMI, shoulder circumferences, waist, hips and lower leg (p< 0.001), and negative associations with the Rodnan skin score (p=0.012) and the cumulative dose of GC (p=0.001).
Conclusion. 87% of patients with SSc had pathological phenotypes of body composition, among them combined phenotypes were significantly more common than in people without rheumatic diseases. BMD in the proximal hip, BMI, circumference of the shoulder, waist, hips and lower leg were positively, and the Rodnan skin score and cumulative dose of GC were negatively associated with the appendicular muscle mass.
Background: The identification of genetic factors that are simultaneously responsible for the predisposition to the development of cardiovascular diseases (CVD) and osteoporosis (OP) is important for the prevention of both conditions.
Aim: The aim of this study is to evaluate three genetic risk scales (GRS) that previously showed an association with bone mineral density (BMD) and fracture risk, as well as to study the associations of these GRS with vascular wall pathology.
Materials and methods: 250 female outpatients (aged 45 to 69) were enrolled into a cross-sectional study. The intima-media thickness (IMT), the presence and number of atherosclerotic plaques (AP) were studied using duplex scanning. Pulse wave velocity (PWV), augmentation index (AI) were measured by applanation tonometry. Coronary vessels calcium deposits were registered by multispiral computed tomography (MSCT) using the Agatston calcium index (CI). The BMD of the spine, hip neck (HN) and proximal hip (PH) was measured using double energy x-ray absorptiometry. Bone resorption marker type-1 collagen C-terminal telopeptide (CTx) was assessed solid-phase enzyme immunoassay. The genetic study included DNA extraction from whole blood samples. Targeted sequencing was performed on the Nextseq550 sequencer (Illumina, USA). Statistical analysis was carried out using the SAS software package for Windows, version 9.0 (SAS Institute Inc., USA).
Results: The chance of detecting low bone mass increased more than 4 times at values of IMT ≥0.9 mm (OR=4.17; 95%CI [1.2–14.4], p<0.02), 2.4 times in the presence of AP in the carotid arteries (OR=2.45; 95%CI [1.12–4.88], p><0.05), by 6.7 times with an Agatstone CI ≥ 100 units (OR=6.68; 95%CI [1.56–28.7], p><0.001), 1.4 times (OR=1.43; 95%CI [0.56–3.68], p><0.438) with a PWV ≥10 m/s, 1.2 times (OR=1.2; 95%CI [0.601–2.43], p><0.60) with increased AI ≥ 27%. According to multivariate linear regression analysis (adjusted for age, duration of postmenopause, marker of bone resorption CTx), a significant association of all GRS with BMD in all parts of the skeleton was revealed. Both univariate and multivariate regression models adjusted for several covariants (age, total cholesterol, systolic blood pressure) showed a reliable association of GRS62 with the presence of plaques and GRS63 — with coronary artery CI. Conclusion: The results of the study demonstrated the association of polygenic genetic risk of GRS-based OP with BMD and vascular wall status indicators in women in the peri and postmenopausal periods.>< 0.02), 2.4 times in the presence of AP in the carotid arteries (OR=2.45; 95%CI [1.12–4.88], p< 0.05), by 6.7 times with an Agatstone CI ≥ 100 units (OR=6.68; 95%CI [1.56–28.7], p< 0.001), 1.4 times (OR=1.43; 95%CI [0.56–3.68], p< 0.438) with a PWV ≥10 m/s, 1.2 times (OR=1.2; 95%CI [0.601–2.43], p<0.60) with increased AI ≥ 27%. According to multivariate linear regression analysis (adjusted for age, duration of postmenopause, marker of bone resorption CTx), a significant association of all GRS with BMD in all parts of the skeleton was revealed. Both univariate and multivariate regression models adjusted for several covariants (age, total cholesterol, systolic blood pressure) showed a reliable association of GRS62 with the presence of plaques and GRS63 — with coronary artery CI.>< 0.60) with increased AI ≥ 27%. According to multivariate linear regression analysis (adjusted for age, duration of postmenopause, marker of bone resorption CTx), a significant association of all GRS with BMD in all parts of the skeleton was revealed. Both univariate and multivariate regression models adjusted for several covariants (age, total cholesterol, systolic blood pressure) showed a reliable association of GRS62 with the presence of plaques and GRS63 — with coronary artery CI.
Conclusion: The results of the study demonstrated the association of polygenic genetic risk of GRS-based OP with BMD and vascular wall status indicators in women in the peri and postmenopausal periods.
Short Report
The Russian Association on Osteoporosis was established in 1995 and by now it has regional branches in 53 cities of the Russian Federation with total 116 members. The Association also includes the Society of Patients OSTEORUS (Chairman — OB Ershova). Association and OSTEORUS are full members of the Committee of National Societies of the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF).
At the general meeting of regional branch delegates, held in September 2020, the following members of the presidium were elected: President prof. OM Lesnyak (St. Petersburg), vice-president prof. OB Ershova (Yaroslavl), members of the presidium: dr. AF Akhatov (Kazan), prof. IA Baranova (Moscow), PhD ZE Belaya (Moscow), IG Belenky (St. Petersburg), KYu Belova (Yaroslavl), LP Evstigneeva (Yekaterinburg), IE Zazerskaya (St. Petersburg), EG Zotkin (Moscow), PhD NA Ibragimova (Omsk), TL Karonova (St. Petersburg), IN Kiseleva (Cheboksary), prof. AYu Kochish (St. Petersburg), fellow of the Russian Academy of Sciences prof. VI Mazurov (St. Petersburg), PhD LA Marchenkova (Moscow), prof. LV Menshikov (Irkutsk), PhD RZ Nurlygayanov (Ufa), prof. EN Otteva (Khabarovsk), prof. SS Rodionova (Moscow), prof. LYa Rozhinskaya (Moscow), IA Skripnikova (Moscow), prof. ON Tkacheva (Moscow), NV Toroptsova (Moscow), prof. SV Yureneva (Moscow). The next meeting of the RAOP Presidium was held on December 18, 2021, at which the results of work in 2021 were summed up and plans for 2022 were outlined.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0).
ISSN 2311-0716 (Online)